Before you can try out the examples below, you must install xyzOPT on your computer: You need a computer with windows 11. Download the xyzOPT installation file from the download area of this website and run this file for installation.
Download the folder, copy to desktop and unzip. This folder contains two files (a .xls-file and a .xml-file) for each of the three examples described below.
Example 1: a machine scheduling problem
Problem description
Consider a company producing toilet paper. The company is having a number of machines on which the paper is produced. Each machine can work in one or more of the following modes: two-ply paper, three-ply paper, four-ply paper. If the mode of a machine is changed, it must be taken into account, that the machine needs to pause for one time step.
The problem is, how to produce a certain demand for the different types of paper on the available machines while minimizing the production time.
Example
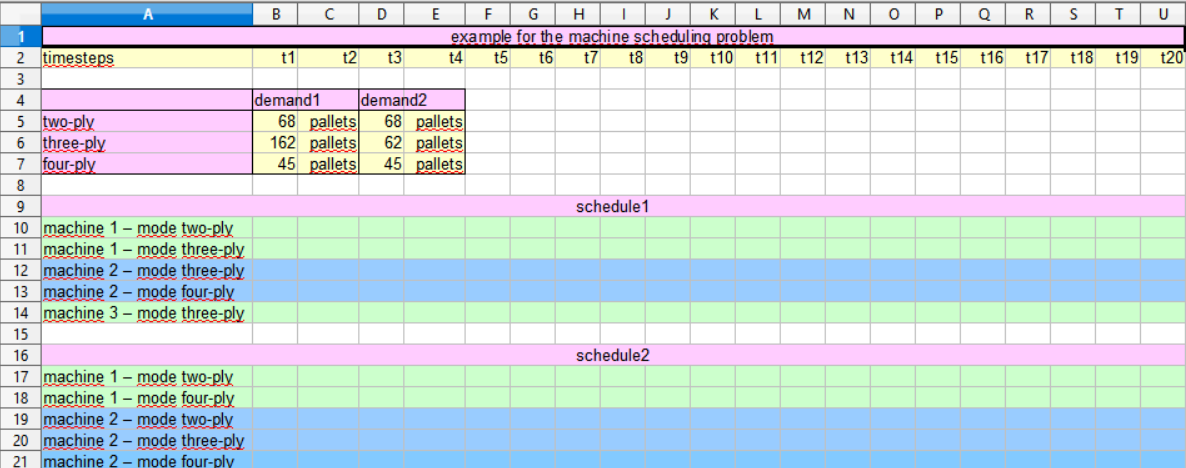
Please open the file machineschedulingproblem.xls in a spreadsheet program, which supports the .xls format:
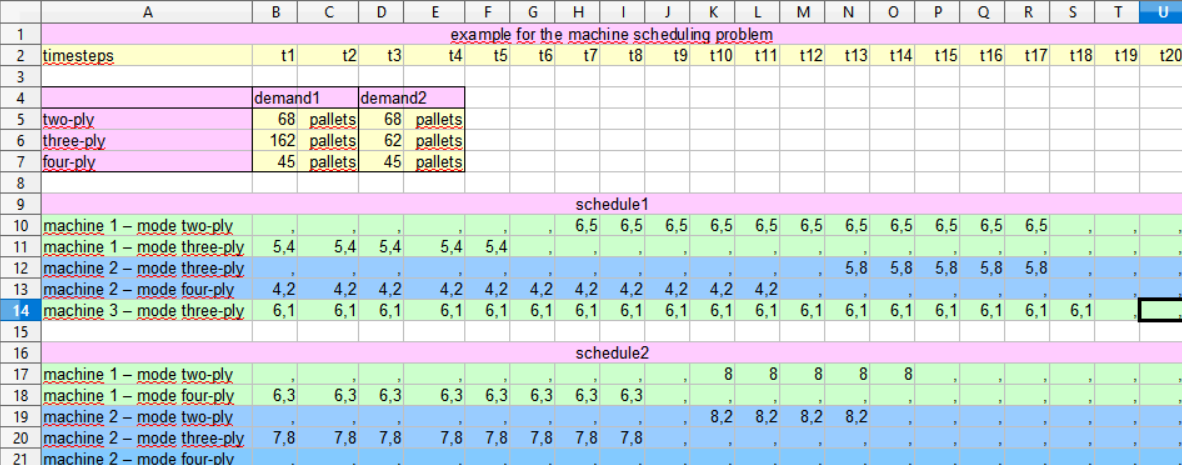
The sheet examplemsp contains the inputdata (namely demand1 and demand2) of two instances of the problem as well as two tables for the results (namely schedule1 and schedule2). In the first instance three machines are available in the second only two.
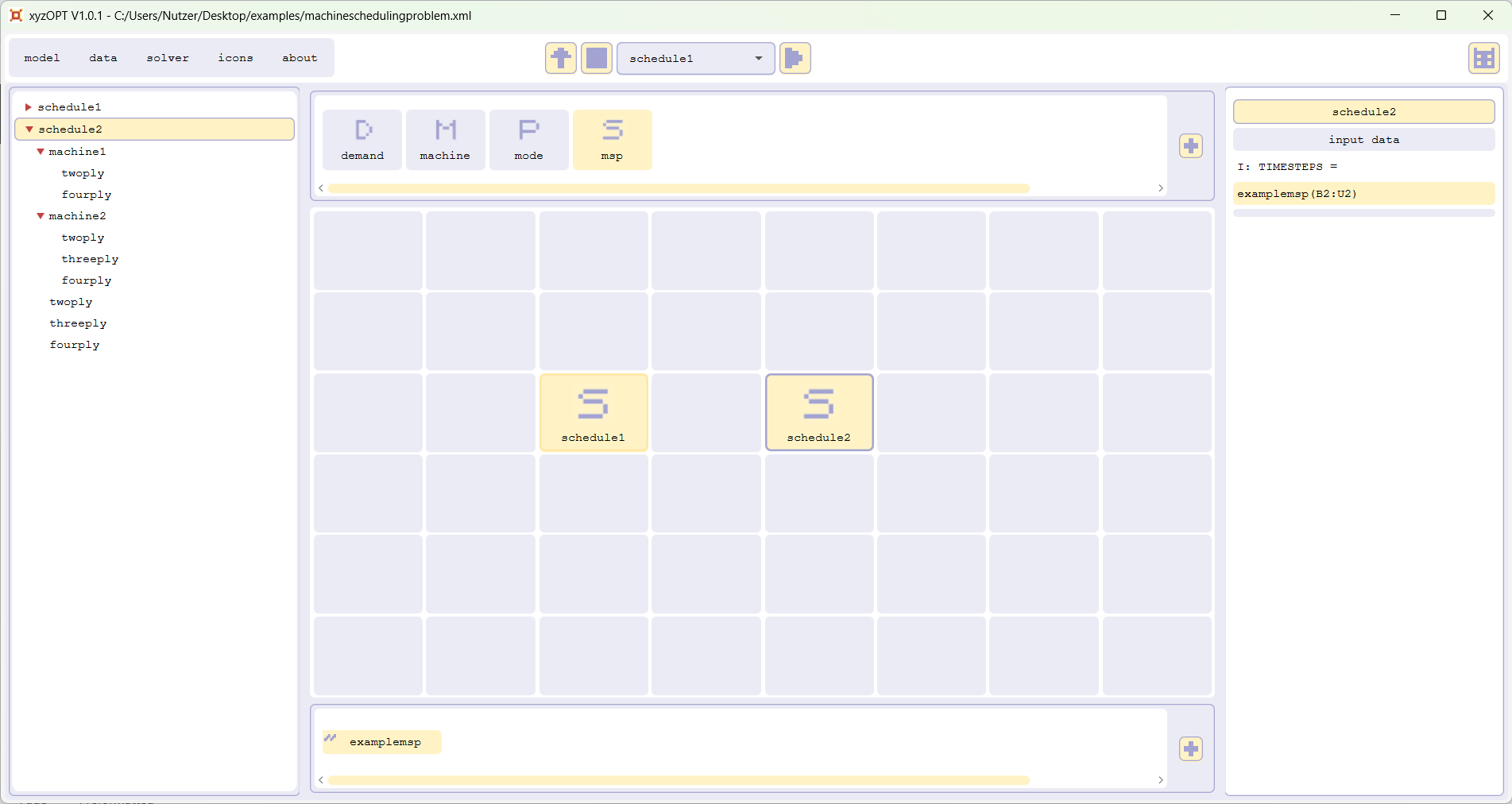
Calculate schedule1 with xyzOPT (for beginners)
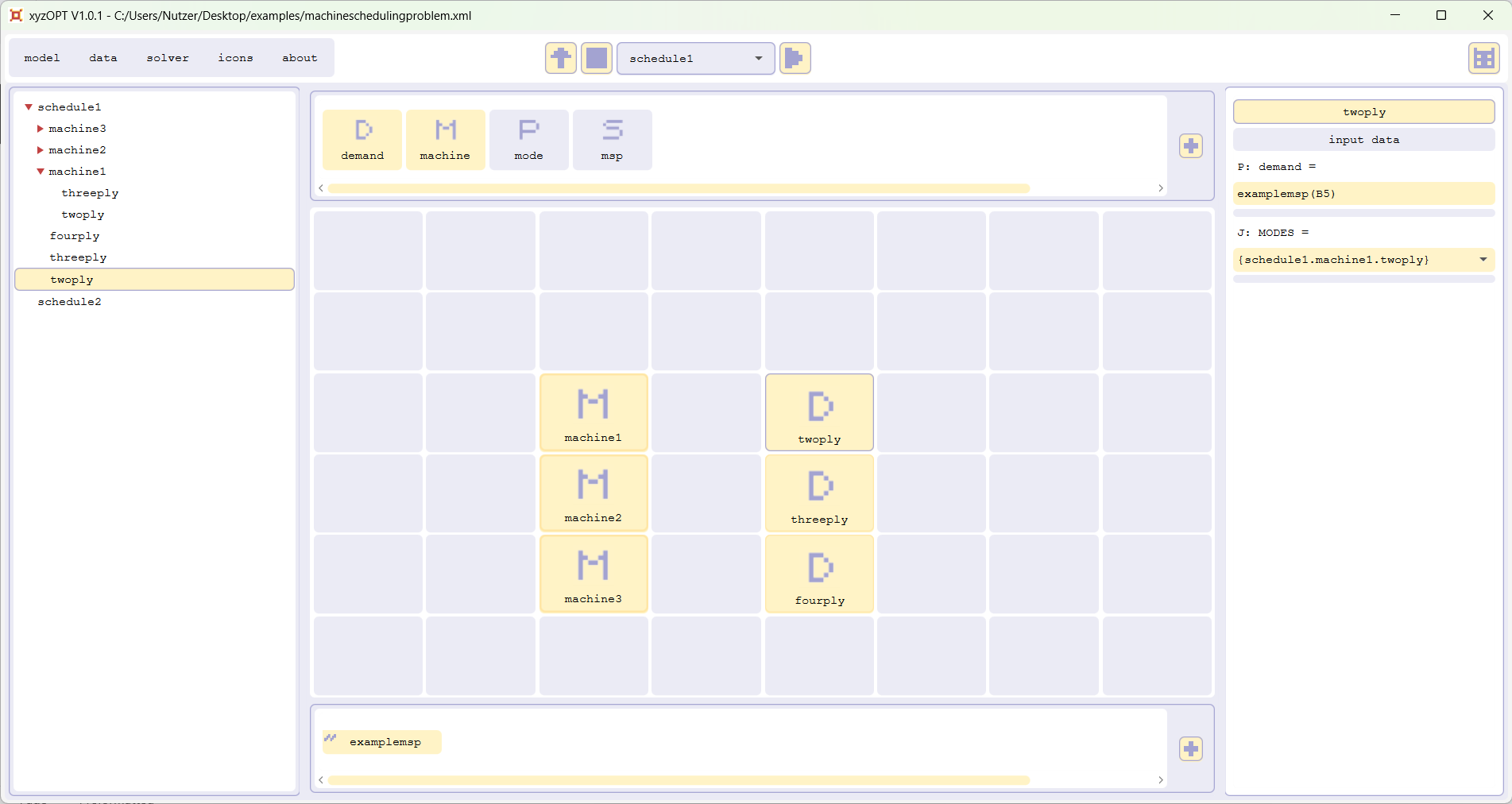
Please start xyzOPT and open the model machineschedulingproblem.xml:
The sheet examplemsp links input data and results between xyzOPT and the sheet examplemsp of the spreadsheet machineschedulingproblem.xls.
The structure as well as the input data is already configured to calculate schedule1: Within the model tree on the left hand side you can see the structure of the instance of the problem. By clicking the items in the grid, the data is displayed in the data box on the right hand side. For each mode of a machine the amount of paper produced per time step, in case the machine is operating in this mode, is already given. The demand for the different paper types is imported.
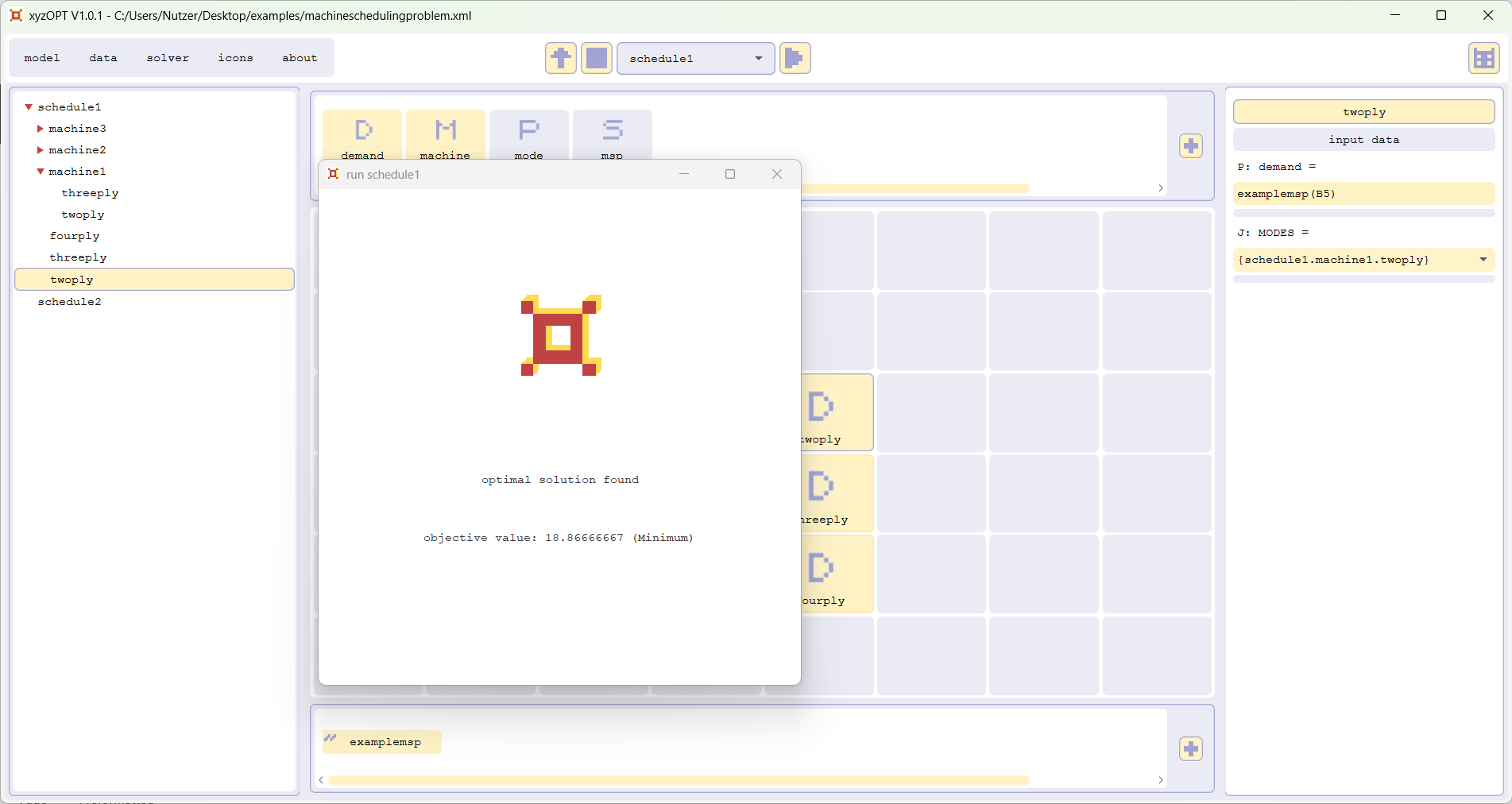
Select schedule1 within the selectionbox in the top and press the run button. The optimization of schedule1 is carried out by xyzOPT; a dialog informs you on the progress of the optimization; you should end up with the following result:
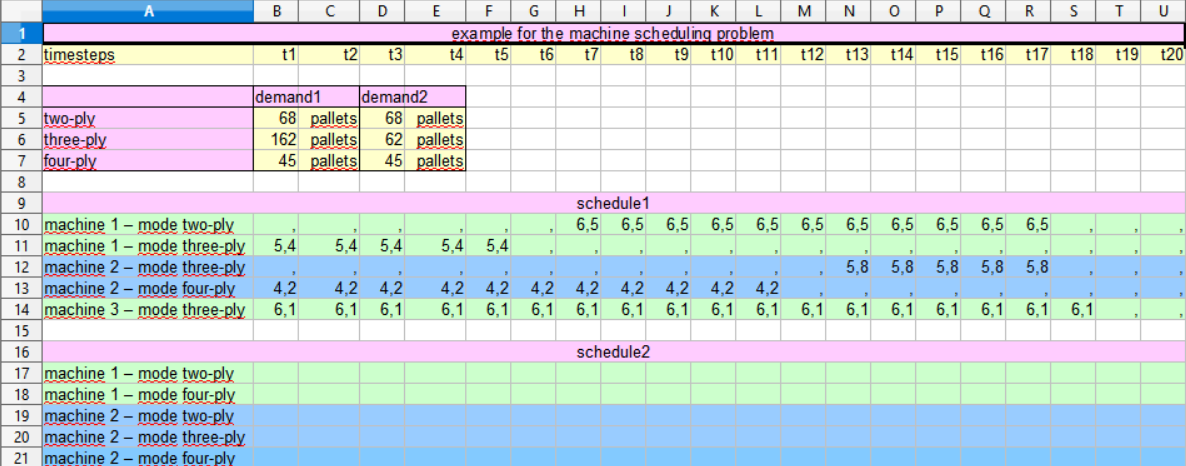
To see the result open machineschedulingprobelm.xls:
Since the solution of the problem might not be unique, your solution might differ from the one given above.Calculate schedule2 with xyzOPT (for beginners)Please select schedule2 in the model tree. Schedule2 still needs to be modelled. Zoom into schedule2 by double clicking. Next add the two machines machine1 and machine2 per drag and drop to the grid. Add the three demand-types next to the two machines. First zoom into machine1 and add the two modes of machine1 and next zoom into machine2 and add the three modes of machine2.
It's still necessary to configure the amountOfPaperProducedPerTimestep for each mode of each machine, the demand and the results need to be linked to the sheet examplemsp.
I have chosen the following values for the amountOfPaperProducedPerTimestep:
machine1.twoply 8.0
machine1.fourply 6.3
machine2.twoply 8.2
machine2.threeply 7.8
machine2.fourply 6.1
To link the demand for each type of paper enter the name of the sheet examplemsp followed by the position in the .xls-file. Example: examplemsp(D5).
For each demand per type of paper the modes of the machines being able to produce the type need to be chosen from the dropdown-menu MODES.
The results are linked per mode per machine. Example: examplemsp(B17:U17).
On my computer running schedule2 led to the following result:
Example 2: room planning for a school
Problem description
Consider a school that has a number of teachers, a number of courses to be taught by the teachers, and a number of rooms in which the courses are to be taught. It is already determined which teacher teaches which course, but each course must be assigned to a room. If a course can consist of more than one lesson, each lesson of the course should be taught in the same room if possible.
Example
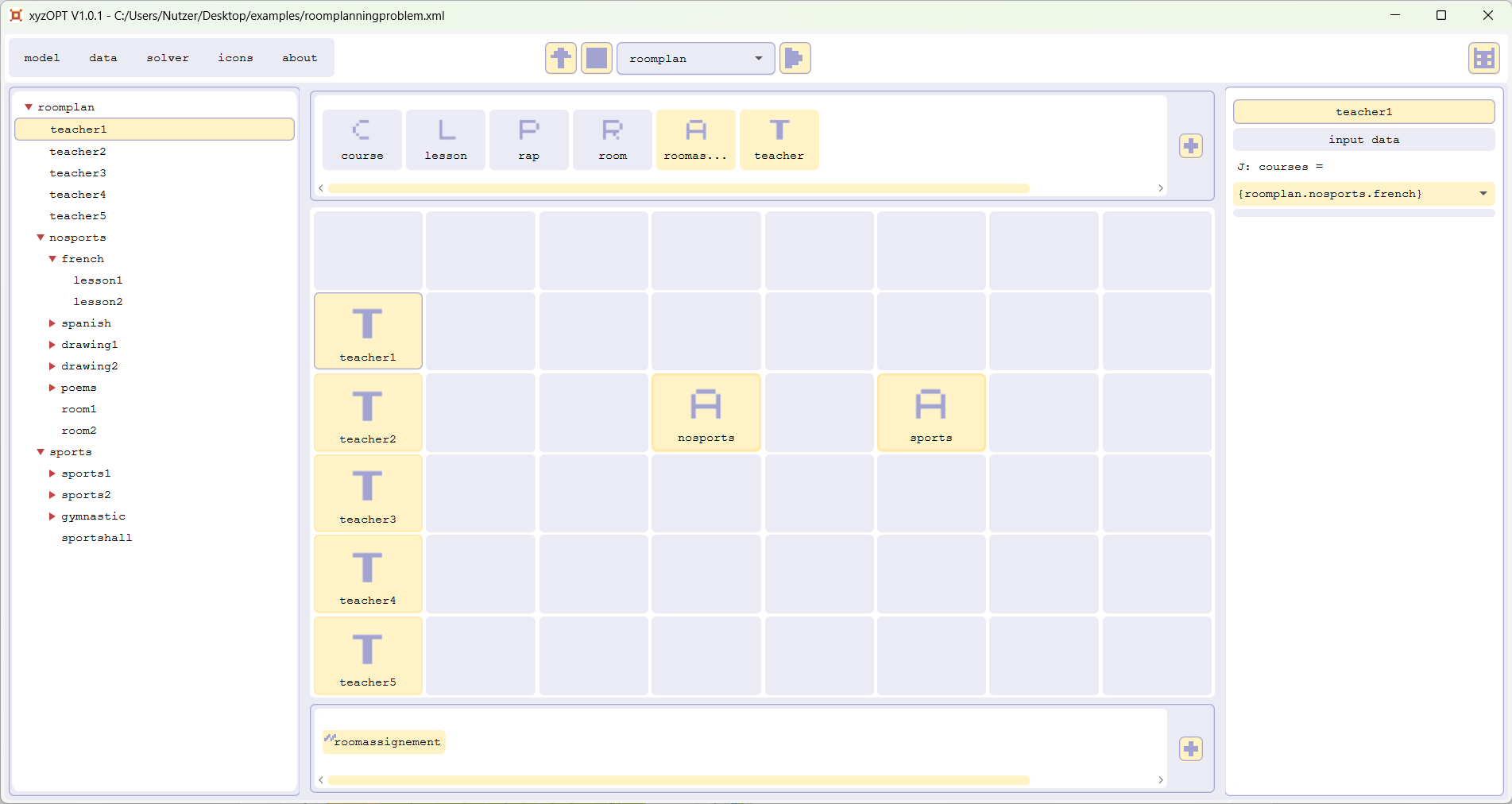
Please open the file roomplanningproblem.xml:
It shows a model with five teachers, who teach a number of courses that are to be allocated to the rooms room1, room2 and the sportshall.
Calculate a roomplan with xyzOPT (for beginners)
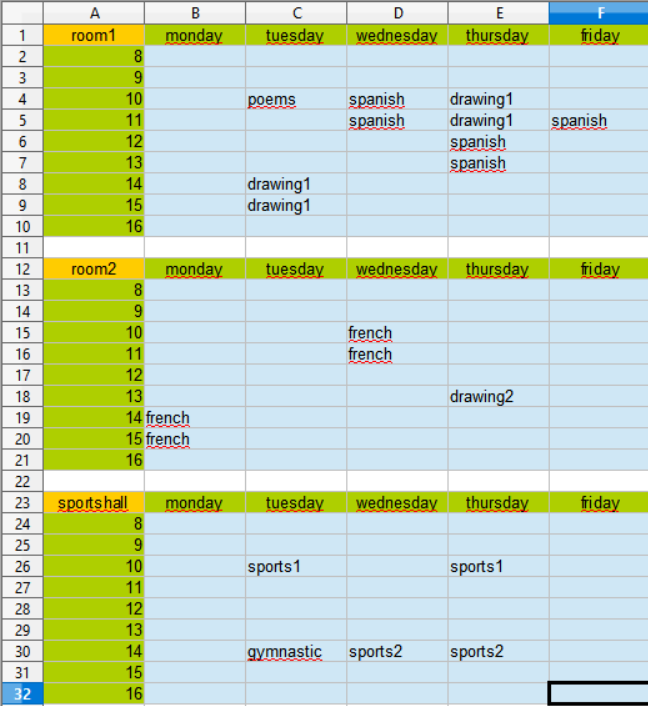
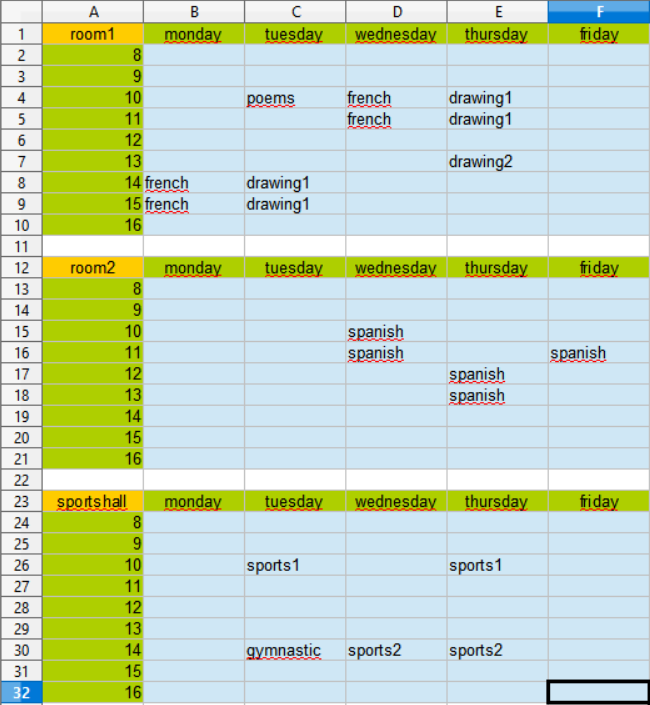
Please run roomplan. To see the result open roomplan.xls:
Calculate a roomplan with one of the rooms having a projector with xyzOPT (for specialists)
Assume that the french and poems course require a projector and only room1 has a projector.
Step 1: add the information, whether a room has a projector
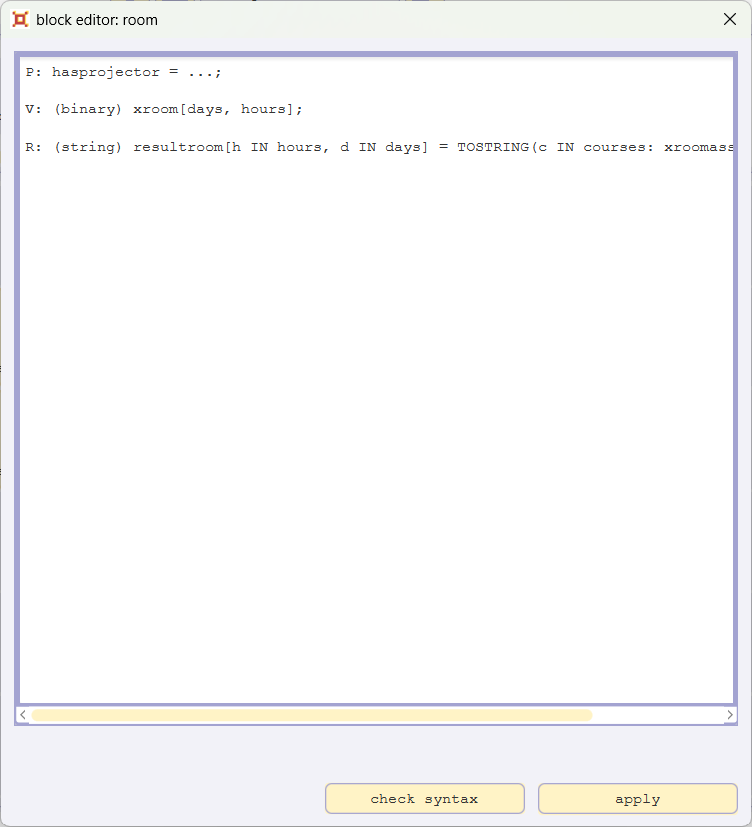
Please open the blockeditor for the block room by double-clicking the block room, add the line
P: hasprojector = ...;
and confirm with apply.
Choose the data of room1. Please enter 1.0 in the field hasprojector. Choose the data of room2 and sportshall and enter 0.0 in the field hasprojector.
Step 2: add the information, whether a course needs a projector
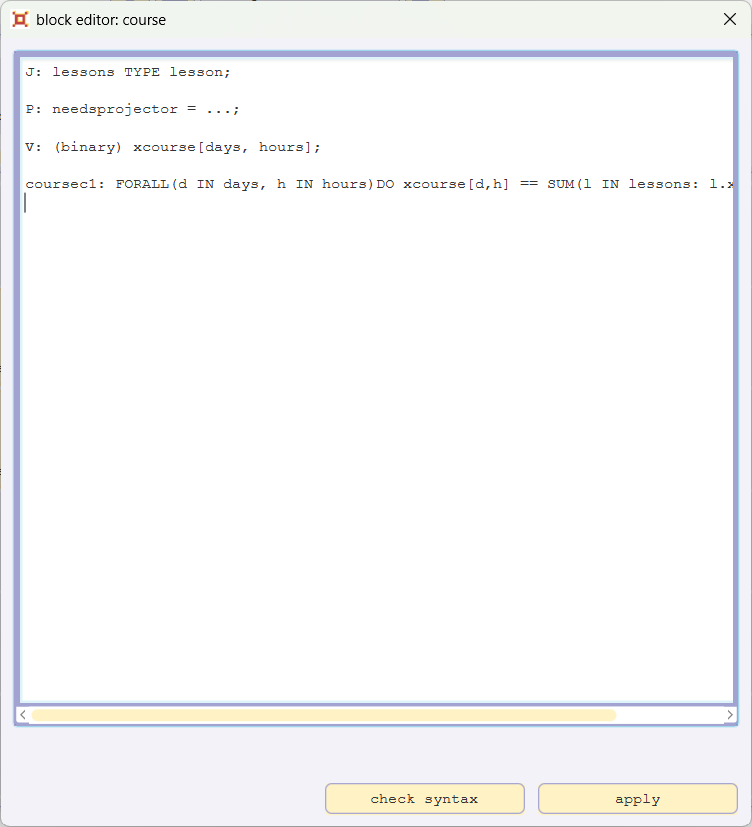
Please open the blockeditor for the block course, add the line
P: needsprojector = ...;
and confirm with apply.
Choose the data of french and poetry and enter 1.0 in the field needsprojector. For all other courses enter 0.0.
Step 3: add the rule, that courses which need a projector are planned in a room that has a projector
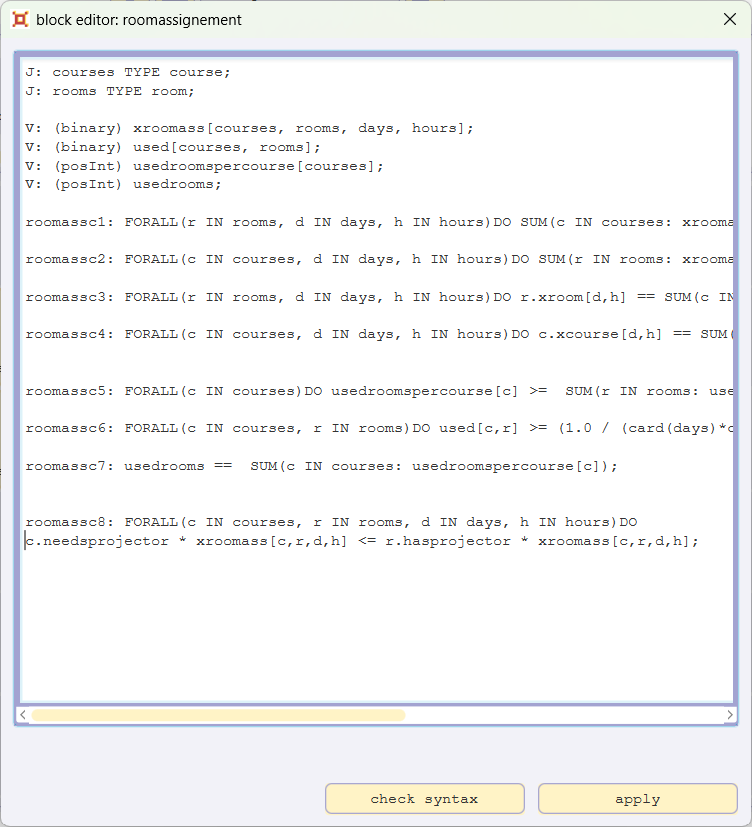
Open the blockeditor for roomassignement and add
roomassc8: FORALL(c IN courses, r IN rooms, d IN days, h IN hours)DO c.needsprojector * xroomass[c,r,d,h] <= r.hasprojector * xroomass[c,r,d,h]
and confirm with apply.
Please run roomplan. To see the result open roomplan.xls again.
Example 3: choose a pokerhand
Problem description
Consider a classical poker game played with 52 cards, in which each player gets seven cards. The problem is to choose the highest combination for one of the players out of the seven cards.
Example
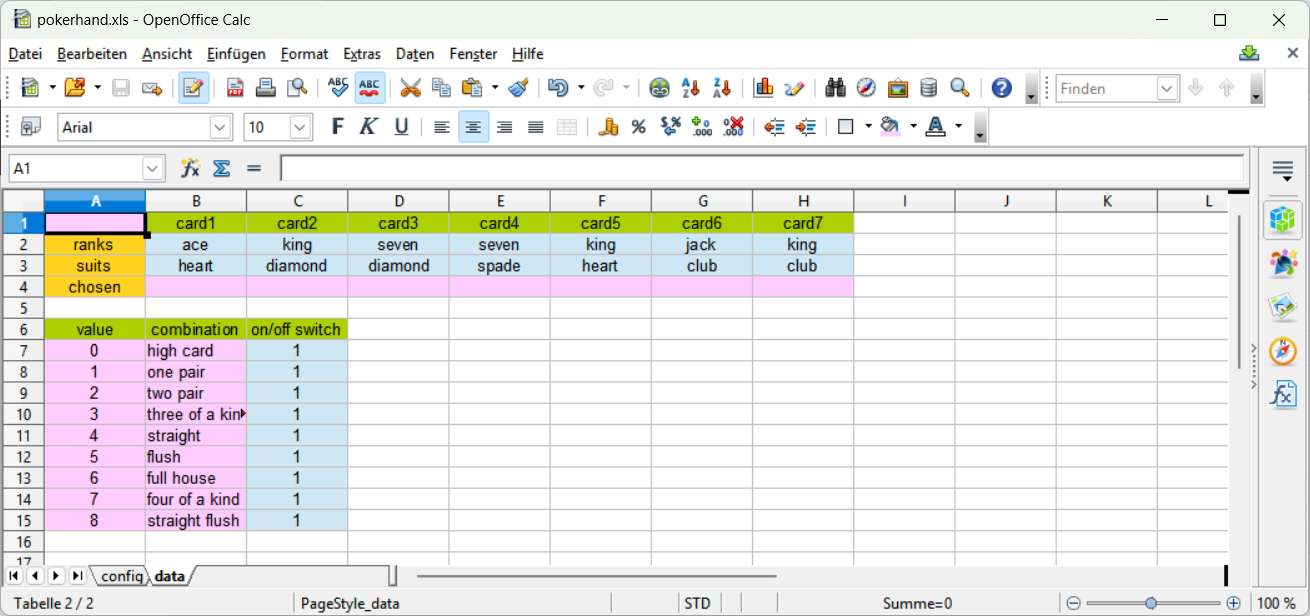
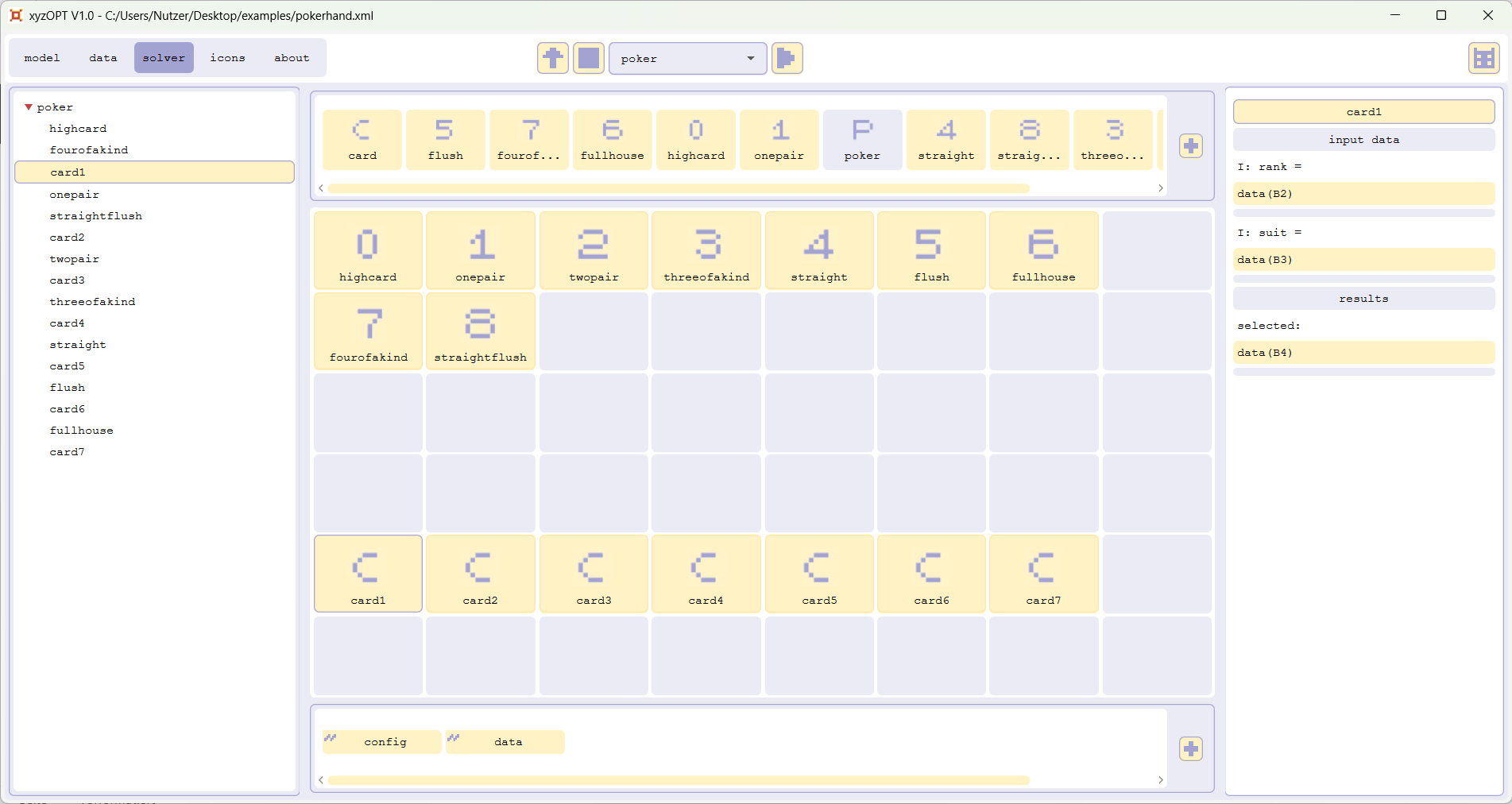
In the cells B2:H2 the ranks of each of the seven cards and in the cells B3:H3 the suits of the seven cards on hand can be entered. The result is written to A1 and to B4:H4 (A1 displays the value of the chosen combination according to the table in the bottom).Calculate a pokerhand with xyzOPT (for beginners)
Recalculate the pokerhand in case the player doesn't want to choose for the combination full house
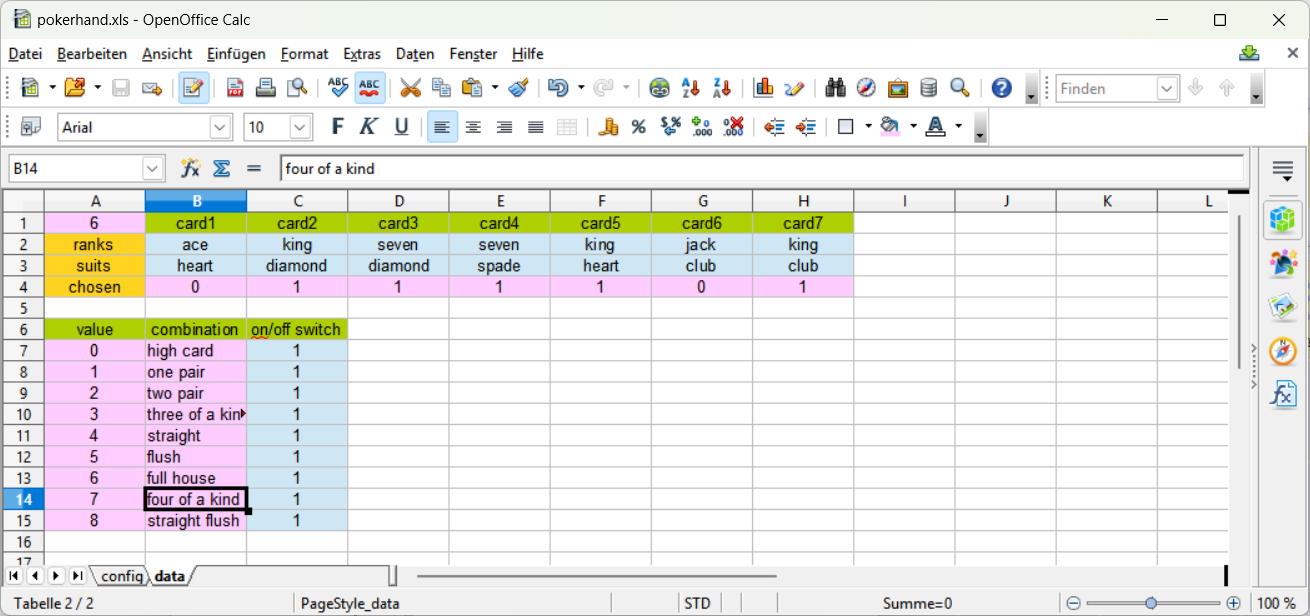
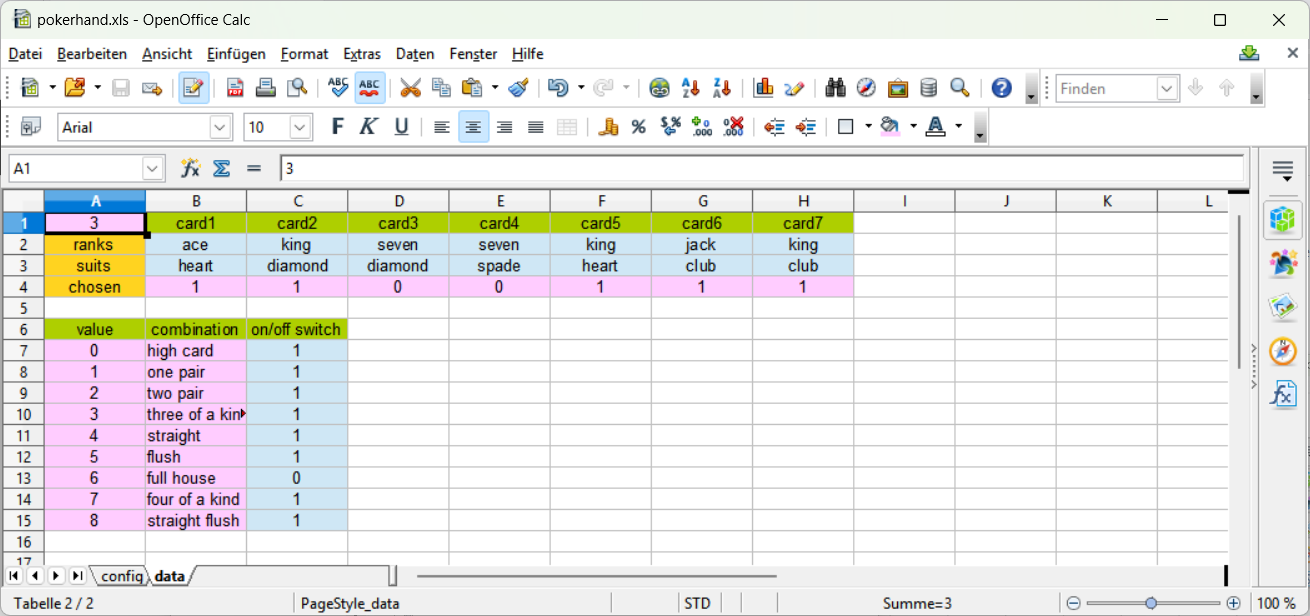
Please insert the value 0.0 into the cell C13 and run poker again.
The next highest combination is to choose three of a kind with card1 and card6 as kickers.